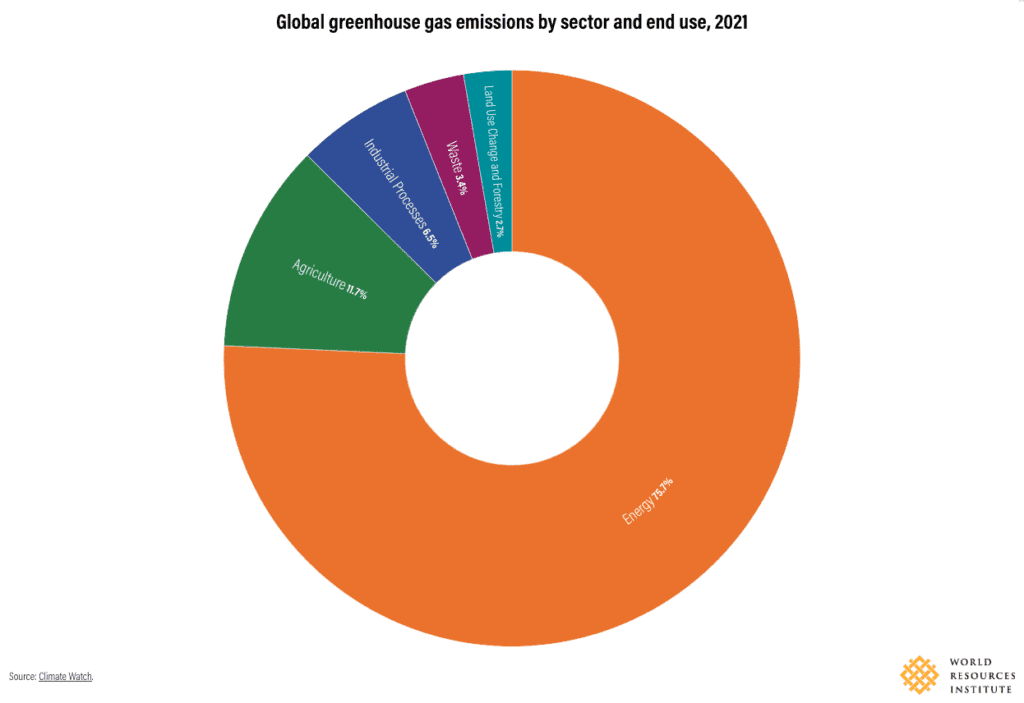
Key Takeaways:
- Energy is the largest emitter: Responsible for 75.7% of global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, with electricity, heat, and transportation as major contributors.
- Industrial emissions are growing fastest: Emissions from industrial processes surged 225% since 1990, outpacing other sectors.
- Data-driven action is crucial: Understanding sectoral emissions is essential for effective climate policies and mitigation strategies.
Breaking Down Global Emissions by Sector
GHG emissions primarily come from five economic sectors:
- Energy (75.7%): The dominant source, including electricity and heat (29.7%), transportation (13.7%), manufacturing and construction (12.7%), and buildings (6.6%).
- Agriculture (11.7%): Emissions stem from livestock farming, manure management, and soil degradation.
- Industrial processes (6.5%): Includes chemical and cement production emissions, excluding energy use.
- Waste (3.4%): Methane and nitrous oxide emissions from landfills and wastewater.
- Land Use, Land-Use Change, and Forestry (2.7%): Accounts for both emissions from deforestation and carbon removals through reforestation.
Industrial Emissions Are Rising Fast
Since 1990, the most rapidly increasing emissions sources include:
- Industrial processes (+225%)
- Electricity and heating (+88%)
- Transportation (+66%)
- Manufacturing and construction (+60%)
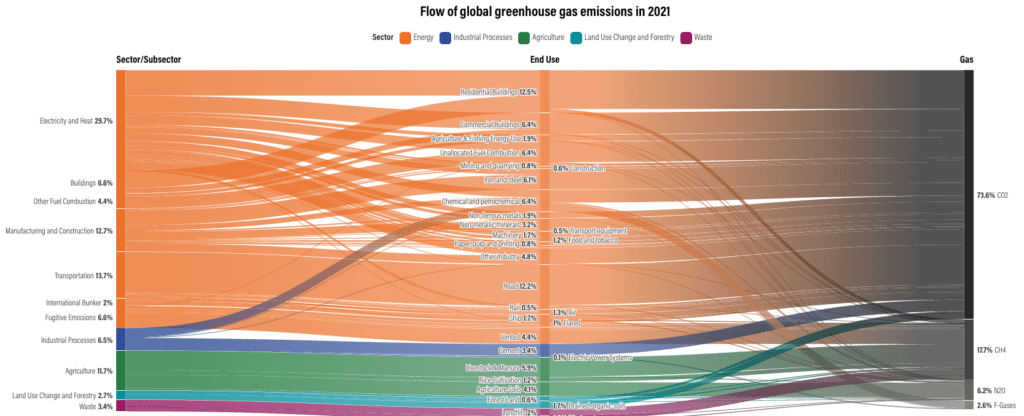
These trends highlight the urgent need for cleaner industrial technologies and sustainable energy systems.
The Role of Carbon Dioxide and Super-Pollutants
- CO₂ dominates emissions (74%), with 92% of it linked to fossil fuel use.
- Methane (CH₄) and nitrous oxide (N₂O)—primarily from agriculture and waste—have significantly higher short-term warming potential than CO₂.
- Fluorinated gases (HFCs, PFCs, SF₆, NF₃) from industrial activities contribute to climate change but in smaller volumes.
The Path Forward: Urgent Emissions Reductions Needed
To limit global temperature rise to 1.5°C, emissions must drop 42% by 2030 and 57% by 2035. Current policies are far from achieving these targets, projecting less than 1% reduction in the same timeframe.
Solutions for Major Emitting Sectors
- Energy: Phasing out coal, scaling up renewables, and improving energy efficiency.
- Transportation: Shifting to low-carbon fuels and electrification.
- Agriculture: Reducing methane emissions from livestock and improving soil management.
- Forestry: Halting deforestation and expanding carbon sequestration efforts.
Access to clear emissions data is critical for designing effective climate strategies. Governments and industries must prioritize high-emitting sectors while implementing rapid, economy-wide transformations.
Related Article: Carbon Capture vs. Renewables: The True Cost of Cutting Emissions

 Follow SDG News on LinkedIn
Follow SDG News on LinkedIn